News & Events
The Heart of Control: Exploring the Efficiency and Versatility of Block Valves in Industrial Applications
Release time: 2025-01-07
The Heart of Control: Exploring the Efficiency and Versatility of Block Valves in Industrial Applications
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Block Valves
2. Understanding the Functionality of Block Valves
2.1 The Mechanism Behind Block Valves
2.2 Types of Block Valves
3. Applications of Block Valves in Industries
3.1 Oil and Gas Industry
3.2 Water Treatment Facilities
3.3 Chemical Processing
4. Advantages of Using Block Valves
4.1 Enhanced Flow Control
4.2 Reliability and Durability
5. Key Considerations When Choosing Block Valves
5.1 Material Selection
5.2 Size and Pressure Ratings
6. Maintenance of Block Valves
6.1 Regular Inspection Practices
6.2 Common Issues and Troubleshooting
7. Future Trends in Block Valve Technology
8. Conclusion
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Introduction to Block Valves
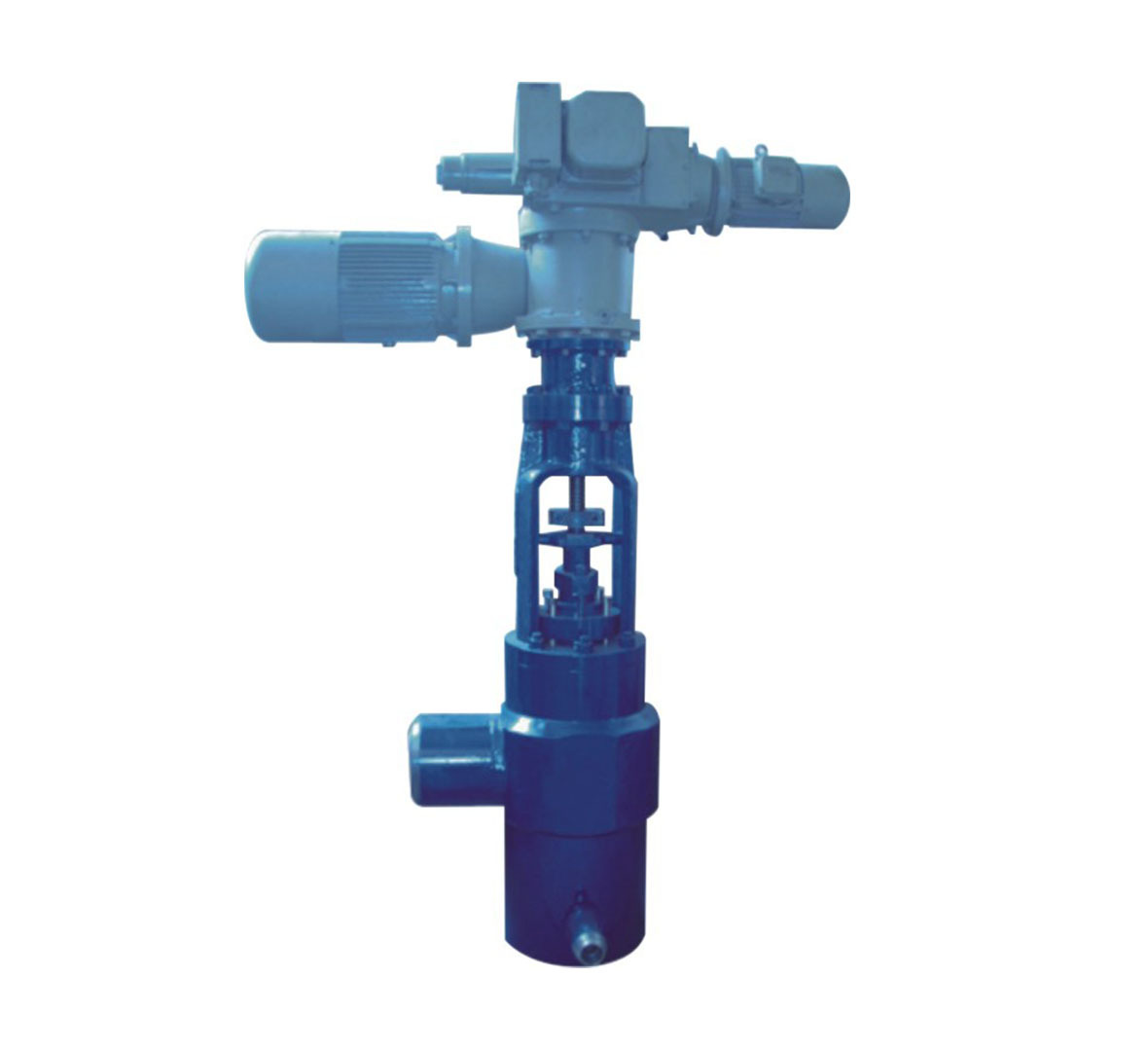
Block valves play a pivotal role in the industrial sector, serving as critical components for managing fluid flow. These valves are designed to either allow or prevent the passage of fluids or gases through pipes, ensuring safe and efficient operation in various applications. In this guide, we will explore the intricate functionality of block valves, their types, and their indispensable role in modern industrial processes.
2. Understanding the Functionality of Block Valves
Block valves serve as the heart of fluid control systems. They are essential for isolating sections of piping and controlling the flow of substances.
2.1 The Mechanism Behind Block Valves
The basic mechanism of a block valve relies on a gate or disc that opens or closes to control flow. When the valve is in the open position, the fluid can pass through with minimal resistance. Conversely, when the valve is closed, it creates a seal that prevents flow. This functionality is vital for applications requiring precise control of fluids.
2.2 Types of Block Valves
There are several types of block valves, each designed for specific applications. The most common include:
- **Gate Valves**: Ideal for on/off control with minimal pressure drop.
- **Globe Valves**: Suitable for throttling flows, providing fine control over fluid movement.
- **Ball Valves**: Known for their quick operation and excellent sealing capabilities.
- **Butterfly Valves**: Lightweight and compact, ideal for larger pipes where space is limited.
3. Applications of Block Valves in Industries
Block valves are integral in various industries, each utilizing these components to ensure safety and efficiency.
3.1 Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas sector, block valves are used for isolating sections of pipelines and managing flow rates. Their reliability is crucial for preventing leaks and maintaining safety in hazardous environments.
3.2 Water Treatment Facilities
Block valves play a crucial role in water treatment plants, allowing operators to control the flow of water through different treatment processes. They help in isolating pumps and tanks during maintenance activities, ensuring smooth operations.
3.3 Chemical Processing
In chemical processing plants, block valves are essential for controlling the flow of raw materials and finished products. Their ability to withstand corrosive substances makes them vital in this sector.
4. Advantages of Using Block Valves
The implementation of block valves in industrial applications offers numerous benefits.
4.1 Enhanced Flow Control
Block valves provide precise control over fluid flow, enabling facilities to optimize their processes. This improves efficiency and can lead to significant cost savings.
4.2 Reliability and Durability
Constructed from robust materials, block valves are designed to withstand harsh conditions. Their durability ensures long service life with minimal maintenance, making them a cost-effective choice for industrial applications.
5. Key Considerations When Choosing Block Valves
Selecting the right block valve is critical for ensuring optimal performance in any system.
5.1 Material Selection
The material of the valve should be compatible with the fluid it will control. Common materials include stainless steel, brass, and plastic, each offering different properties suited for specific environments.
5.2 Size and Pressure Ratings
Choosing the correct size and pressure rating is vital for preventing leaks and ensuring the valve operates effectively within the system.
6. Maintenance of Block Valves
Proper maintenance is essential for the longevity and functionality of block valves.
6.1 Regular Inspection Practices
Conducting regular inspections can help identify potential issues before they escalate. It's crucial to check for leaks, corrosion, and any other signs of wear and tear.
6.2 Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Some common issues with block valves include leaks and difficulty in operation. Troubleshooting these problems often involves inspecting seals and replacing worn components.
7. Future Trends in Block Valve Technology
As technology evolves, so does the design and functionality of block valves. Innovations in automation and smart technology are poised to enhance their efficiency. Remote monitoring and control systems are becoming more prevalent, allowing for improved management of fluid systems.
8. Conclusion
Block valves are indeed the heart of fluid control in various industrial applications. Their ability to efficiently manage flow and pressure is vital for maintaining operational integrity and safety. By understanding the functionality, applications, and advantages of block valves, industries can make informed decisions that enhance productivity and longevity.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the primary function of a block valve?
Block valves primarily control the flow of fluids or gases through piping systems, allowing for isolation and management of fluid movement.
2. How do I choose the right block valve for my application?
Consider factors such as fluid compatibility, pressure ratings, and the specific requirements of your system when selecting a block valve.
3. What maintenance practices should I follow for block valves?
Regular inspections, checking for leaks, and ensuring the valve operates smoothly are essential maintenance practices.
4. What materials are block valves typically made from?
Common materials include stainless steel, brass, and plastic, chosen based on the fluid and operating conditions.
5. Can block valves be automated?
Yes, many modern block valves can be integrated with automation technologies for remote monitoring and control, improving efficiency in operations.
Keywords: Block Valve
 sales@cnmxv.cn
sales@cnmxv.cn
 86-577-67389088
86-577-67389088